Written by Anneri Fourie | Marketing Executive
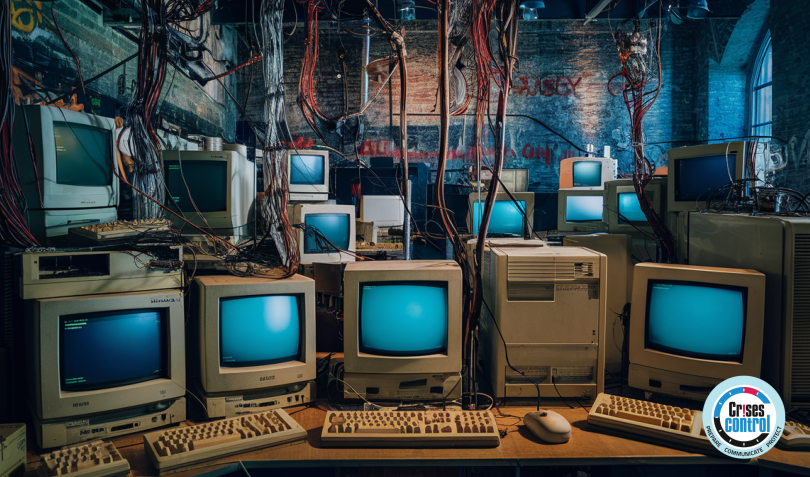
In today’s digital landscape, technology forms the backbone of virtually every business operation. Yet, many organisations continue to rely on ageing technology infrastructure, unaware of the ticking time bomb it represents. The consequences of this can be disastrous—leading to operational disruptions, financial losses, and compromised security.
This blog will explore the challenges posed by outdated IT systems, discuss the critical need for preparedness, and show how Crises Control can help mitigate these risks with advanced Crisis Management Software and Early Warning Systems.
Understanding Ageing Technology Infrastructure
What Constitutes Ageing Technology Infrastructure?
Ageing technology infrastructure refers to outdated or obsolete IT systems that businesses continue to use despite their diminishing efficiency and growing risks. This can include legacy hardware, unsupported software, and systems that are no longer compatible with modern security protocols.
Why do companies persist with these ageing systems?
The reasons vary—some businesses aim to avoid the costs and complexities of upgrading, while others are unaware of the potential dangers posed by relying on outdated technology. However, the short-term savings or perceived simplicity of maintaining old systems can lead to significant, long-term consequences.
Key Indicators of Ageing IT Systems
Identifying ageing technology infrastructure early can help in mitigating risks before they escalate into major crises. Here are some signs your IT systems may be past their prime:
- Frequent Downtime: Increased system failures and unplanned outages.
- Slower Performance: Reduced efficiency and longer response times.
- Incompatibility with New Software: Difficulty integrating with modern applications or platforms.
- Increased Maintenance Costs: Higher expenses for repairs, patches, and workarounds.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Exposure to cyber threats due to outdated security features.
Recognising these indicators is the first step toward addressing the underlying issues and preparing your business for potential disruptions.
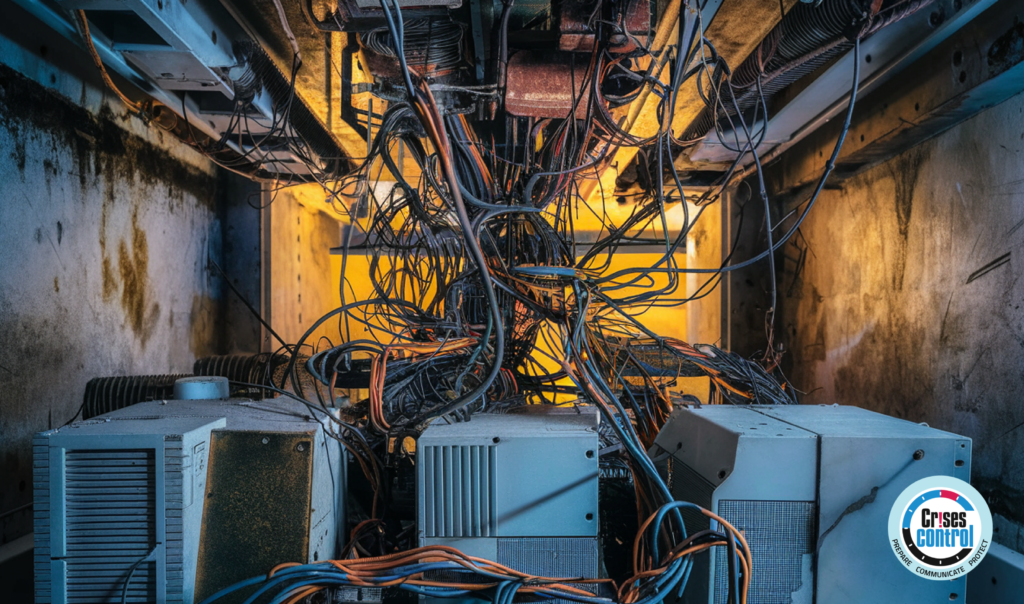
The Consequences of an IT Meltdown
Operational Disruptions
An IT meltdown can bring business operations to a grinding halt. Imagine your critical systems failing at a crucial moment—customer service lines go down, transaction processing is interrupted, and vital data becomes inaccessible. These disruptions not only stall day-to-day operations, but also damage your reputation and customer trust.
For businesses in sectors like finance, healthcare, or e-commerce, where uptime is critical, the effects of such an event can be devastating. Even a few hours of downtime can lead to significant financial losses and a lasting impact on client relationships.
Financial Implications
The financial consequences of relying on ageing technology infrastructure extend beyond the immediate costs of an IT meltdown. Companies may face hefty expenses for emergency repairs, data recovery, and system restoration. Additionally, there are hidden costs such as lost revenue, diminished employee productivity, and the potential need for legal settlements if customer data is compromised.
A study by the Ponemon Institute found that the average cost of IT downtime is around $5,600 per minute. For small to medium-sized businesses, these costs can quickly escalate, putting significant financial strain on the organisation.
Increased Security Risks
Ageing IT systems often lack the robust security measures needed to fend off modern cyber threats. As technology evolves, so do the tactics of cybercriminals, making outdated systems prime targets for attacks. Data breaches, ransomware, and other cyber incidents can have severe consequences, including the loss of sensitive information, legal penalties, and irreversible damage to your brand’s reputation.
Moreover, compliance with industry regulations often requires up-to-date systems that can protect against emerging threats. Failing to upgrade can lead to non-compliance, resulting in fines and legal repercussions.

Preparing for an IT Meltdown
Conducting a Thorough Risk Assessment
The first step in preparing for an IT meltdown is to understand the vulnerabilities within your current infrastructure. Conducting a thorough risk assessment will help you identify which systems are most at risk, what the potential impacts of a failure might be, and how you can mitigate these risks. This process should involve:
- Inventorying All IT Assets: Catalogue all hardware, software, and network components to understand their age and condition.
- Assessing Vulnerabilities: Identify weak points in your infrastructure, particularly those related to security, performance, and reliability.
- Prioritising Risks: Focus on critical systems that are essential for your business operations and most susceptible to failure.
Developing a Robust Crisis Management Plan
Once you have identified the risks, it’s essential to develop a comprehensive crisis management plan that addresses potential IT meltdowns. This plan should include:
- Communication Protocols: Establish clear lines of communication for internal teams and external stakeholders during a crisis.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Ensure that you have reliable data backup solutions and a clear recovery plan to minimise downtime.
- Contingency Plans: Develop alternative procedures to keep operations running if primary systems fail.
- Regular Testing: Conduct tabletop exercises and drills to test your crisis management plan and make necessary adjustments.
Investing in Modernisation
While maintaining ageing technology infrastructure may seem cost-effective in the short term, the long-term risks and costs far outweigh the initial savings. Investing in modern, reliable systems is crucial to ensure your business can withstand potential IT meltdowns.
Modernisation should not only focus on replacing outdated hardware and software, but also on integrating solutions that enhance your overall IT resilience. This includes adopting cloud-based systems, implementing advanced security protocols, and ensuring that your technology is scalable to meet future demands.
How Crises Control Can Help
Proactive Monitoring and Early Warning Systems
Crises Control offers a suite of tools designed to monitor your IT infrastructure in real-time, providing early warnings of potential issues before they escalate into a full-blown crisis. With automated notifications and escalation procedures, your team can respond swiftly to any emerging threats, minimising downtime and disruption.
Our Early Warning System is equipped to detect anomalies and trigger alerts that allow you to take preemptive action, ensuring that your business remains operational even in the face of IT challenges.
Robust Crisis Management Software
Crises Control’s Crisis Management Software is specifically designed to help businesses develop, store, and execute comprehensive crisis management plans. Our platform allows you to create detailed response strategies tailored to your specific needs, ensuring that your team is prepared for any scenario.
With Crises Control, you can streamline communication, coordinate response efforts, and manage resources effectively during a crisis. Our software integrates seamlessly with existing systems, providing a bridge to modernised infrastructure without the need for a complete overhaul.
Ensuring Business Continuity
One of the key features of Crises Control is its ability to maintain business continuity even when primary systems fail. Our cloud-based platform ensures that critical functions, such as communication and data access, remain operational regardless of the status of your on-premises infrastructure.
This means that, in the event of an IT meltdown, your business can continue to serve customers, manage operations, and protect its reputation. Crises Control’s resilience and reliability provide peace of mind, knowing that your business is safeguarded against the risks posed by ageing technology infrastructure.
Conclusion
Ageing technology infrastructure poses significant risks to businesses, from operational disruptions and financial losses to increased security threats. However, by conducting thorough risk assessments, developing robust crisis management plans, and investing in modernisation, companies can mitigate these risks and ensure their long-term viability.
Crises Control offers the tools and expertise needed to navigate the challenges of ageing IT systems. Our proactive monitoring, early warning systems, and crisis management software are designed to keep your business running smoothly, even in the face of IT meltdowns.
Don’t wait for a crisis to strike. Prepare your business today by partnering with Crises Control. Contact us to get a free personalised demo and see how we can help you safeguard your operations and future-proof your technology infrastructure.
Request a FREE Demo